The field effect tube of the inverter works in a switching state, and the current flowing through the tube is very large. If the tube selection is inappropriate, the driving voltage amplitude is not large enough, or the circuit heat dissipation is not good, the field effect tube will generate heat.
- Inappropriate selection of field effect transistors
The field effect transistor in the inverter works in a switching state, which usually requires its drain current to be as large as possible and its on-resistance to be as small as possible, thereby reducing the saturation voltage drop of the tube, thereby reducing the consumption and heat generation of the tube.
Consulting the field effect tube manual, we will find that the higher the withstand voltage value of the field effect tube, the greater its on-resistance. The on-resistance of those tubes with large drain current and low withstand voltage value is generally less than tens of milliliters. Europe.
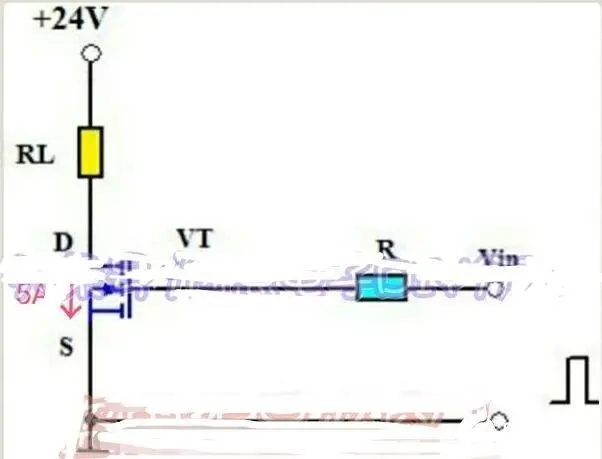
Assuming that the load current in Figure 1 is 5A, we can choose the field effect transistor RU75N08R commonly used in inverters (see above) and the IRF840 with a withstand voltage of 500 volts. Their drain currents are all greater than 5A. However, the on-resistances of the two tubes are different, and driving the same current, their heating values are very different. The on-resistance of the RU75N08R is only 0.008, while the on-resistance of the IRF840 is 0.85. When the load current flowing through the tube is all 5A, the tube voltage drop of RU75N08R is only 0.04V, and the tube consumption of FET is only 0.2W at this time, while the tube voltage drop of IRF840 can reach 4.25W, and the tube consumption is as high as 21.25W. From It can be seen that the smaller the on-resistance of the field effect transistor of the inverter, the better. Tubes with large on-resistance will consume a lot under high current.
- The driving voltage amplitude of the driving circuit is not large enough
A field effect transistor is a voltage controlled device. In order to reduce tube consumption and heat generation, the driving voltage of the field effect transistor gate should be large enough and the edge of the driving pulse should be steep, which can reduce tube voltage drop and tube consumption. - The field effect tube does not dissipate heat well.
Since the field effect transistor of the inverter has a large tube loss, the heat sink is usually required to have a large enough external area during operation, and the external heat sink should be in close contact with the heat sink of the field effect transistor itself (usually coated with thermally conductive silicon fat). If the external heat sink is small or does not make close contact with the heat sink of the field effect transistor itself, the tube will generate heat.
Leave a Reply